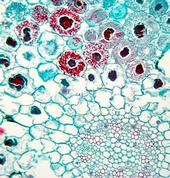
Mycorrhizae are symbiotic associations that form between the roots of most plant species and fungi. These symbioses are characterized by bi-directional movement of nutrients where carbon flows to the fungus and inorganic nutrients move to the plant, thereby providing a critical linkage between the plant root and soil. In infertile soils, nutrients taken up by the mycorrhizal fungi can lead to improved plant growth and reproduction. As a result, mycorrhizal plants are often more competitive and better able to tolerate environmental stresses than are nonmycorrhizal plants.Mycorrhizal associations vary widely in form and function. Ectomycorrhizal fungi are mostly basidiomycetes that grow between root cortical cells of many tree species, forming a Hartig net. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi belong to the order Glomales and form highly branched structures called arbuscules, within root cortical cells of many herbaceous and woody plant species.Plant responses to colonization by mycorrhizal fungi can range from dramatic growth promotion to growth depression. Factors affecting this response include the mycorrhizal dependency of the host crop, the nutrient status of the soil, and the inoculum potential of the mycorrhizal fungi.
(stolen from: http://cropsoil.psu.edu/sylvia/mycorrhiza.htm)
Musically, Mycorrhiza is a result of the sound experimentations between the projects Szbutä Soröh, from Brazil and Basidiomycota, from Los Angeles. A lengthy track is available for download over Myspace and more material is fast approaching.