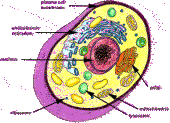
Hi. I am the cell. I am in every living thing. I am very small. There are two kinds of cell. Plant and animal. In the animal cell you will find: Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Chromatin, Centrioles, Mitochondria, Cytosol, Centrosome, Smooth and Rough Endo. Reticulum, Ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, Vacuoles, Microfilaments, Microtubules, Lysosomes, Peroxisomes, and Cytoskeleton.
In a plant cell you will find all of these except for centriole and lysosomes. In the plant cell you also gain a cell wall chloroplasts, and chlorophyl.Cell Membrane-a thin membrane (a double layer of lipids) enclosing the cytoplasm of a cell; proteins in the membrane control passage of ions (like sodium or potassium or calcium) in and out of the cell; "all cells have a cell membrane"
Cytoplasm-The jellylike material that makes up much of a cell inside the cell membrane, and, in eukaryotic cells, surrounds the nucleus.
Nucleus-the part of a plant or animal cell that controls its development. contains DNA and RNA
Chromatin-the readily stainable substance of a cell nucleus consisting of DNA and RNA and various proteins; during mitotic division it condenses into chromosomes
Centrioles-One of two cylindrical cellular structures that are composed of nine triplet microtubules and form the asters during mitosis.
Mitochondria-an organelle in the cytoplasm of cells that functions in energy production. the power house of the cell
Cytosol-The fluid component of cytoplasm, excluding organelles and the insoluble, usually suspended, cytoplasmic components.
Centrosome-A small region of cytoplasm adjacent to the nucleus that contains the centrioles and serves to organize microtubules.
Endoplasim Reticulum-a network of tubular membranes within the cytoplasm of the cell, occurring either with a smooth surface (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) or studded with ribosomes (rough endoplasmic reticulum), involved in the transport of materials.
Ribosomes-Small cellular components composed of specialised ribosomal RNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Golgi Apparatus-an organelle, consisting of layers of flattened sacs, that takes up and processes secretory and synthetic products from the endoplasmic reticulum and then either releases the finished products into various parts of the cell cytoplasm or secretes them to the outside of the cell
Vacuoles-A small cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell, bound by a single membrane and containing water, food, or metabolic waste.
Microfilaments-Any of the minute fibers located throughout the cytoplasm of cells, composed of actin and functioning primarily in maintaining the structural integrity of a cell
Microtubules-Any of the tube-shaped protein structures that help eukaryotic cells maintain their shape and assist in forming the cell spindle during cell division. Microtubules and actin filaments are the main components of the cell's supporting the cytoskeleton.
Lysosomes-A membrane-bound organelle in the cytoplasm of most cells containing various hydrolytic enzymes that function in intracellular digestion
Peroxisomes-A cell organelle containing enzymes, such as catalase and oxidase, that catalyze the production and breakdown of hydrogen peroxide.
Cytoskeleton-The internal framework of a cell, composed largely of actin filaments and microtubules.
Cell Wall-the definite boundary or wall that is part of the outer structure of certain cells, as a plant cell.
Chloroplasts-Plant cell inclusion bodies that contain chlorophyll. They occur in cells of leaves and young stems.
Chlorophyl-Any of a group of green pigments that are found in the chloroplasts
Background from Yahoo search result